…the student and lover of nature has this advantage over people who gad up and down the world, seeking some novelty and excitement; he has only to stay at home and see the procession pass. The great globe swings round to him like a revolving showcase; the change of seasons is like the passage of strange and new countries; the zones of the earth, with all their beauties and marvels, pass one’s door and linger long in the passing…. I sit here among the junipers of the Hudson, with purpose every year to go to Florida, or to the West Indies, or to the Pacific coast, yet the seasons pass and I am still loitering, with a half-defined suspicion, perhaps, that, if I remain quiet and keep a sharp lookout, these countries will come to me.
AFTER THREE QUITE OBSCURE NATURE WRITERS, I THOUGHT IT WAS TIME TO VISIT FAMILIAR GROUND, SO I PULLED MY VOLUME OF BURROUGHS DOWN FROM THE SHELF. Granted, many casual natural history readers forget “the other John”, recalling from this time period only John Muir (who, like Burroughs, sported a white beard and spoke exultantly of nature’s marvels). The two, though, are remarkably different. John Muir was a mountain prophet, speaking in tones of religious rapture about his beloved Sierra Nevada fastnesses. John Burroughs, on the other hand, grew up and lived out his days in the Catskills of New York State, keeping close to the Hudson River. Muir walked long distances alone in the mountains and climbed a redwood in a thunderstorm just to feel it rocking in the wind; Burroughs, meanwhile, remarked self-deprecatingly about his own efforts to venture into the wilds. After a particularly difficult short camping trip with a few companions, he observed that “On this excursion…I was taught how poor an Indian I should make, and what a ridiculous figure a party of men may cut in the woods when the way is uncertain and the mountains high.” It must be added that the highest point in the Catskill “Mountains” is Slide Mountain, at 4189 feet; the highest point in the Sierras, Mount Whitney, is 14,505 feet.
JOHN BURROUGHS’ PROSE WANDERS COMFORTABLY THROUGH THAT LIMINAL RURAL SPACE BETWEEN CIVILIZATION AND THE WILD. I would classify him as a ruderal writer, using a term most commonly applied to plants that are the first to colonize ground disturbed by human action, such as an abandoned field. Cattle roam across many a page, and he frequently writes of fields and weeds. My particular copy of this book, the second edition from 1901, features about 50 photographs (all black and white, of course) of John Burroughs in the landscape and at home. Most of his out-of-door images show predominantly open farmland dotted with occasional trees. In these familiar haunts, Burroughs encountered, and wrote about, numerous birds, trees, and forbs (flowering ground plants), occasionally drifting into comments about his other “neighbors”, from bumblebees to black bears. In all of his walks, his enduring goal, I think, was to realize himself as more deeply a part of his home landscape, and to more fully understand not only nature, but himself as part of it:
One’s on landscape comes in time to be be a sort of outlying part of himself; he has sowed himself broadcast upon it, and it reflects his own moods and feelings; he is sensitive to the verge of the horizon: cut those trees, and he bleeds; mor those hills, and he suffers…. Man can have but one interest in nature, namely, to see himself reflected or interpreted there; and we quickly neglect both poet and philosopher who fail to satisfy, in some measure, this feeling.
FOR BURROUGHS, KEEPING A SHARP LOOKOUT INVOLVED ALL THE SENSES, NOT JUST THE KEEN EYE. In his essays in this volume (collected from his previous works), Burroughs wrote with equal enthusiasm about the scents and sounds of the fields and woodlands near his home. For instance, writing about early April, he enthusiastically remarked:
Then its odors! I am thrilled by its fresh and indescribable odors — the perfume of the bursting sod, of the quickened roots and rootlets, of the mould under the leaves, of the fresh furrows. No other month has odors like it. The west wind the other day came fraught with a perfume that was to the sense of smell what a wild and delicate strain of music is to the ear. It was almost transcendental.
Speaking of “music to the ear”, here Burroughs describes the sounds of tiny frogs (species not identified) “piping in the marshes” in late April:
…toward the last of the month, there is a shrill musical uproar, as the sun is setting, in every marsh and bog in the land. It is a plaintive sound, and I have heard people from the city speak of it as lonesome and depressing, but to the lover of the country it is a pure spring melody.
BURROUGHS ALSO CELEBRATES SEASONAL CHANGE, AND HOW IT REFLECTED THE NATURE’S INNATE VITALITY. “Does not the human frame yield to and sympathize with the seasons?” he asked the reader, in his essay “Autumn Tides”. Underlying it all, no matter how much insight science can offer us, is an abiding mystery: “The only thing inexplicable is the inherent impulse to experiment, the original push, the principle of Life.”

BURROUGHS IS AT HIS MOST PROFOUND, I FEEL, IN HIS MUSINGS ABOUT SCIENCE AND POETRY. In his written work, he moves comfortably between the two worlds, appreciating their kindred natures. As he explains toward the close of his essay, “A Sharp Lookout”,
You may go to the fields and the woods, and gather fruit that is ripe for the palate without any aid of yours, but you cannot do this in science and in art. Here truth must be disentangled and interpreted — must be made in the image of man. Hence all good observation is more or less a refining and transmuting process, and the secret is to know the crude material when you see it…. Before a fact can become poetry, it must pass through the heart or the imagination of the poet; before it can become science, it must pass through the understanding of the scientist.
THE PACE OF TECHNOLOGICAL CHANGE DURING HIS LIFETIME WAS QUITE DRAMATIC. He was already in his late 20s when the Civil War broke out, but by the last decade of his life he gleefully roamed the countryside in a Model T automobile given to him by Henry Ford. His long life (he died just short of his 84th birthday) spanned America’s transition from a largely agrarian society to a rapidly industrializing one. Yet he maintained a confidence in what science and technology have to offer. I wonder if he would still maintain this outlook if he were alive today?
Science does not mar nature. The railroad, Thoreau found, after all, to be about the wildest road he knew of, and the telegraph wires the best aeolian harp out of doors. Study of nature deepens the mystery and charm because it removes the horizon farther off. We cease to fear, perhaps, but how can one cease to marvel and to love?
BEFORE CLOSING THIS ESSAY, I CANNOT RESIST COMPARING HIS WRITING STYLE WITH THAT OF HIS CONTEMPORARY, EDITH THOMAS. Both of them, it turns out, wrote about gossamer — the slender threads of spider silk festooning the landscape in the autumntime. Thomas actually devoted an entire essay to it, and provides a more detailed picture of the phenomenon than Burroughs does. Here is an excerpt:
During this season [of gossamer summer], …miles and miles of hazy filament (if it could be measured linearly) are floating about in the soft, indolent air. Especially, late in the afternoon, with a level and glowing sun, do these mysterious threads flash out along the ground, horizontally between shrubs, slantwise from grass to tree, or else cut adrift, and sailing as the wind wills…. It takes nothing from the poetry that lies in the weft of the gossamer when it is known to be the work of an unconsidered spider…. By some, it is claimed that this floating web is not spread with predaceous intent, but rather as a means of aerial navigation; indeed, these vague and indeterminate threads would hardly disturb a gnats’ cotillion, if blown in their path. Hitherto, we have regarded the spider as an humble, plodding creature of the earth, an unaspiring, stay-at-home citizen, but this new aeronautic hypothesis hints that the poor insect is a very transcendentalist, an ideal voyager…. Some naturalists assert that the gossamer spider instinctively takes advantage of the levity of the atmosphere, thrusting out its threads until they reach a current of warmer and rarer air, which draws them upward, the spider going along with the uncompleted web. Whether it is capable of cutting short its journey and casting anchor at pleasure is indeed questionable.
And here is gossamer again, this time described by Burroughs:
A peculiar feature of our fall may sometimes be seen of a clear afternoon late in the season. Looking athwart the fields under the sinking sun, the ground appears covered with a shining veil of gossamer. A fairy net, invisible at midday and which the position of the sun now reveals, rests upon the stubble and the spears of grass covering acres in extent — the work of innumerable little spiders. The cattle walk through it, but do not seem to break it. Perhaps a fly would make his mark upon it. At the same time, stretching from the tops of the trees, or from the top of a stake in the fence, and leading off toward the sky, may be seen the cables of the flying spider, — a fairy bridge from the visible to the invisible. Occasionally seen against a deep mass of shadow, and perhaps enlarged by clinging particles of dust, they show quite plainly and sag down like a stretched rope, or sway and undulate like a hawser in the tide.
(A hawser is a thick rope for mooring or towing a ship.)

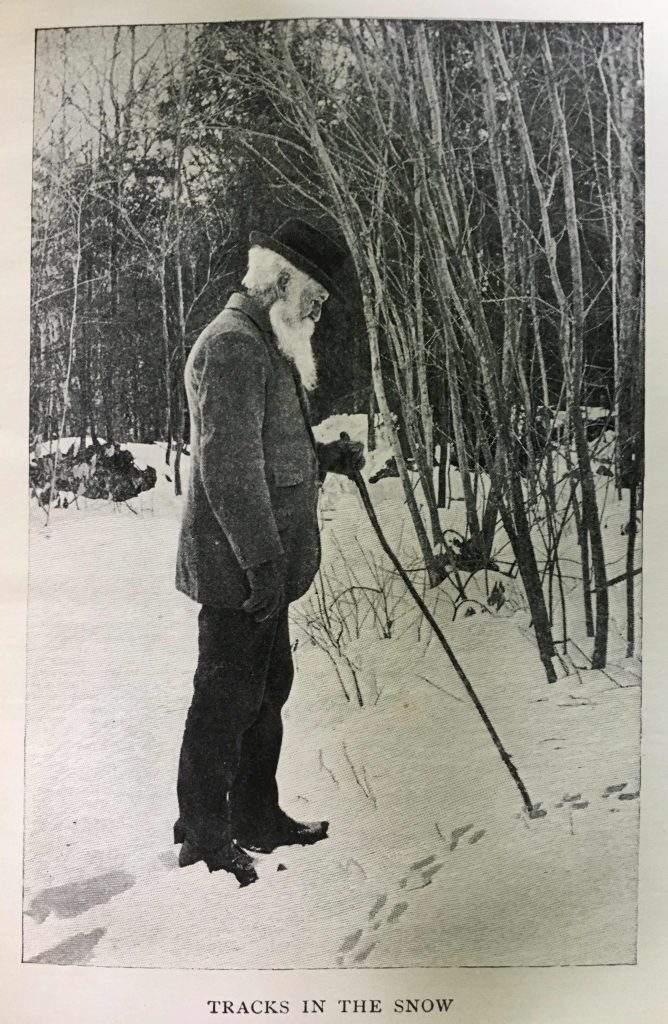
AS A POSTSCRIPT, I WOULD LIKE TO SHARE WHAT I CAN ABOUT MY PARTICULAR VOLUME OF BURROUGHS. I was able to obtain an original second edition from 1901 (augmented by a biographical sketch of Burroughs and the some further photos by Clifton Johnson). It has a lovely gold gilt cover, and includes dozens of photographs of Burroughs, posing on rocks, standing in the doorway of his study, pointing out tracks in the snow with his walking stick, etc. My copy bears almost no marks of its 119-year journey to me, with the notable exception of a normally blank back page filled with text in ink. It is a poem (not inspiring particularly, but a step up from Bradford Torrey’s), entitled “The Lure o’ the Woodland”, attributed to Thomas S. Jones, Jr. Thanks to the marvel of the Internet, I was able to discover that the work originally appeared in Ainslee’s magazine in November, 1907. Unfortunately, every year of the magazine is available online except for 1907. So this transcription of the poem, semi-legible though it is, may be the only copy left in existence. Of the copy-writer, all I know is that his or her initials were JWD, and that he or she was in Jacksonville, Florida on March 19, 1911.