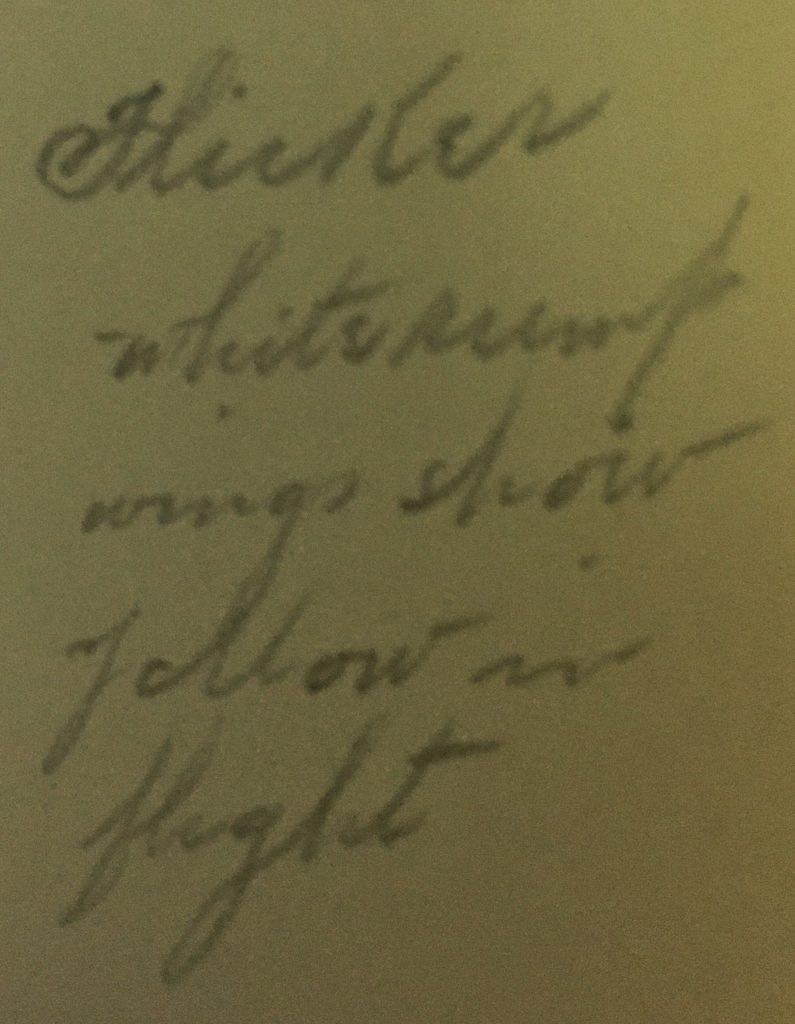The lifeless dun of the close-cropped southward slopes and the tawny tangles of the swales are kindling to living green with the blaze of the sun and the moist tinder of the brook’s overflow.
ROWLAND ROBINSON IS NOT AN EASY AUTHOR TO READ. His sentences sometimes run for a dozen lines on the page, nearly every one a dense thicket of adjectives and nouns with scarcely an adverb in sight. He was taken to reflecting, and rhapsodizing, on the campfire; half a dozen of his essays focus on them. (He is quite taken with fire in general, as the quote above demonstrates.) The volume I read is a collection of short essays, written for the magazine Forest and Stream, an early conservation magazine that merged with Field and Stream in 1930. As such, the works are organized, to a rough approximation, across the seasons of the year. But otherwise, the book has no structure or theme beyond encountering nature in the woods and fields of Vermont. And while his text includes a number of passages in his essays on various animals that could be interpreted as the work of an early conservationist, he falls short of advocating for greater regulations on sport hunting. (In Robinson’s defense, George Bird Grinnell and Theodore Roosevelt are even more famous conservationists who bagged far more game than he did.)
AND YET HIS WRITING SOMETIMES EVOKES SEASONAL MOMENTS OF NATURE IN A VIVID AND BEAUTIFUL WAY. Consider, for instance, that same quote with which I began this essay. Or here is another one, from earlier in the season. Reading it slowly, I am transported there, to see and feel his world of the northern Vermont forest, still gripped by winter but with intimations of springtime, tree trunks decorated by shifting patterns of light and shadow:
The coarse-grained snow is strewn thickly with shards of bark that the trees have sloughed in their long hibernation, with shreds and tatters of their tempest-torn branches. But all this litter does not offend the eye nor look out of place, like that which is scattered in fields and about homesteads. When this three months’ downfall of fragments sinks to the carpet of flattened leaves, it will be at one with it, an inwoven pattern, as comely as the shifting mesh of browner shadows that trunks and branches weave between the splashes of sunshine. Among these is a garnishment of green moss patches and fronds of perennial ferns which tell of life that the stress of winter could not overcome. One may discover, amid the purple lobes of the squirrelcup leaves, downy buds that promise blossoms, and others, callower, but of like promise, under the dusty links of the arbutus chain.
IT IS EASY TO CLASSIFY HIS WRITING AS “FLOWERY” AND DISMISS IT ALTOGETHER. Nowadays, nature writing is not tasked with painting pictures, but instead can accompany them. Robinson was first an artist, and only later in life a writer; surprisingly, this book of nature essays is entirely unillustrated apart from its cover art. Instead, his essays are filled with still-lifes, vivid sentences depicting the landscape and its inhabitants (primarily birds, frogs, and mammals, with a brief nod to a few different plants (like squirrelcup, a.k.a. hepatica, which has cameos in several of the essays). They challenge the frenetic reader of today to slow down and let the words sink in and allow his landscape to appear in the imagination:
At last there is full and complete assurance of spring, in spite of the baldness of the woods, the barrenness of the fields, bleak with sodden furroughs of last year’s ploughing, or pallidly tawny with bleached grass, and untidy with the jetsam of winter storms and the wide strewn litter of farms in months of foddering and wood-hauling.
There is full assurance of spring in such incongruities as a phoebe a-perch on a brown mullein stalk in the midst of grimy snow banks, and therefrom swooping in airy loops of flight upon the flies that buzz across this begrimed remnant of winter’s ermine, and of squirrelcups flaunting bloom and fragrance in the face of an ice cascade, which, with all its glitter gone, hangs in dull whiteness down the ledges, greening the moss with the moisture of its wasting sheet of pearl.
At its best, the result of Robinson’s wordsmithery is a prose poem to the season, fraught with images akin to William Carlos Williams’ poem, Red Wheelbarrow, but far less spartan — more like a scene filled choc-a-bloc with various wheelbarrows, all clamoring for attention at once:
Summer is past its height. The songless bobolink has forsaken the shorn meadow. Grain fields, save the battalioned maize, have fallen from gracefulness and beauty of bending heads and ripple of mimic waves to bristling acres of stubble. From the thriftless borders of ripening weeds, busy flocks of yellowbirds in faded plumage scatter in sudden flight at one’s approach like upblown flurries of dun leaves. Goldenrod gilds the fence corners, asters shine in the dewy borders of the woods, sole survivors of the floral world save the persistent bloom of the wild carrot and succory — flourishing as if there had never been mower or reaper — and the white blossoms of the buckwheat crowning the filling kernels. The fervid days have grown perceptibly shorter, the lengthening nights have a chilly autumnal flavor, and in the cool dusk the katydids call and answer one to another out of their leafy tents, and the delicate green crickets the Yankee folks call August pipers play their monotonous tunes.
VIVID, OR OVERWROUGHT? Rowland walks that line through much of his prose, and my reaction to it depends upon my willingness to absorb his words and enter his world. Either way, though, I can still appreciate him, too, for some of his environmental sentiments. For instance, here he speaks out about the wanton killing of garter snakes, at a time when the killing of animals of any and all kinds was commonplace and often done with little thought of the consequences:
…a moving curved and recurved gleam of gold on black and a flickering flash of red catch your eye and startle you with an involuntary revulsion. With charmed eyes held by this new object, you grope blindly for a stick or stone. But, if you find either, forbear to strike. Do not blot out one token of spring’s awakening nor destroy one life that rejoices in it, even though it be so humble a life as that of a poor garter snake. He is so harmless to man that, were it not for the old, unreasoning antipathy, our hands would not be raised against him; and, if he were not a snake, we should call him beautiful in his stripes of black and gold, and in graceful motion — a motion that charms us in their undulation of waves, in their flickering reflections of sunlight on rushy margins and wooded shores, in the winding of a brook through a meadow, in the flutter of a pennant and the flaunting of a banner, the ripple of wind-swept meadow and grain field, and the sway of leafy boughs.
Robinson continues the scene by imagining that the viewer witnesses the garter snake, newly out of hibernation, catch and swallow a frog. He then suggests that the snake will, in fact, catch and eat many “noxious insect[s] and mice over the course of the year, and thus be of considerable benefit to the farmer. Robinson acknowledges that a garter snake might also feed on some eggs and young of ground-nesting birds, supposedly providing justification for killing the snake. In fact, though, Robinson argues, that is a hypocritical act, because the same person killing the snake probably shoots numerous woodcock and grouse for sport. Robinson closes the scene with these strong and prescient words about the human relationship to nature:
Of all living things, only man disturbs the nicely adjusted balance of nature. The more civilized he becomes, the more mischievous he is. The better he calls himself, the worse he is. For uncounted centuries the bison and the Indian shared a continent, but in two hundred years or so the white man has destroyed the one and spoiled the other.
AT THE SAME TIME, THERE ARE MOMENTS IN HIS WRITING WHEN HE SEEMS WILLING TO EXCUSE SOME OF THE DAMAGE, OR AT LEAST EXPRESSES RESIGNATION TO THE FACT THAT IT IS LIKELY TO CONTINUE. For instance, it is still okay in his book to kill potentially harmful animals, or animals that provide some value to humans. Robinson’s is still an anthropocentric viewpoint, much aligned with the end of the 19th century in America. His essay, A Century of Extermination, bemoans the fate of so many dwindling creatures — bison, passenger pigeons, heath hens. The last two were still living in 1896, though rapidly headed toward extinction. Yet Robinson offers little hope for change, closing the essay with an image of an old man grateful he will not live to see the destruction, and sad when pondering “the poor inheritance of his children.”
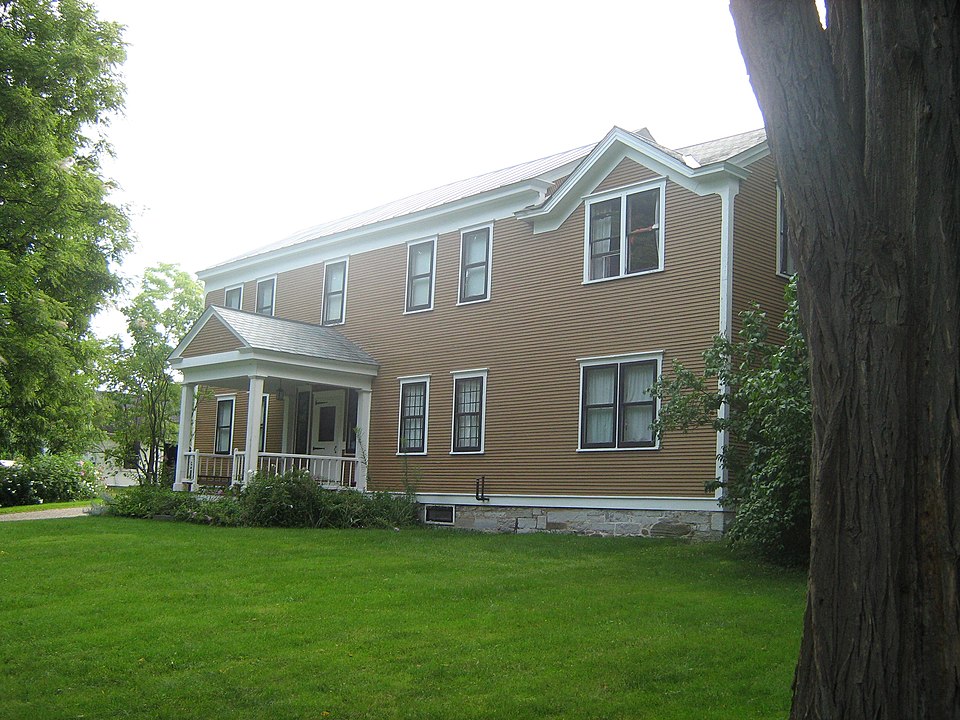

AS A POSTSCRIPT, I OFFER THESE REFLECTIONS ON WHAT PHYSICALLY REMAINS OF ROWLAND ROBINSON’S LIFE AND WORK. I will begin with a photograph of Rokeby in Ferrisburg, Vermont, the home for 200 years of the Robinson family, including Rowland Robinson’s father (a radical abolitionist who used his home as a stop on the Underground Railroad) and Rowland himself. Apart from Gene Stratton-Porter (two of whose homes are preserved and open to the public in Indiana) and John Burroughs (whose cabin and final home are both available for viewing New York), Robinson is only the third of the eight authors with at least one home preserved for posterity. (I might add that efforts are also underway to save Chimney Farm, Henry Beston’s home in Maine after leaving the Outermost House.) Sadly, I have yet to visit any of these places; perhaps I will plan a tour once travel becomes both possible and safe again.
MEANWHILE, I HAVE A FIRST EDITION (ONLY EDITION) OF ROBINSON’S BOOK. My copy is in excellent condition, which, on the flip side, means that there is little I can share of its history. Only one page, the opening of his Golden-Winged Woodpecker essay, contains pencil writing. On the margin, almost a poem, are the words, “Flicker / white rump / wings show / yellow in / flight.” It is comforting to know that at least one reader of this book was not content to encounter nature by armchair, but also sought to encounter its wild inhabitants out-of-doors. Dare I call it a flicker of hope?